Whether you already handle products with gas cylinders or are simply interested in learning more about the necessary safety precautions, this blog post will provide you with valuable insights to protect yourself and others from potential hazards.
What does the gas cylinder pictogram mean?

What are gases under pressure?
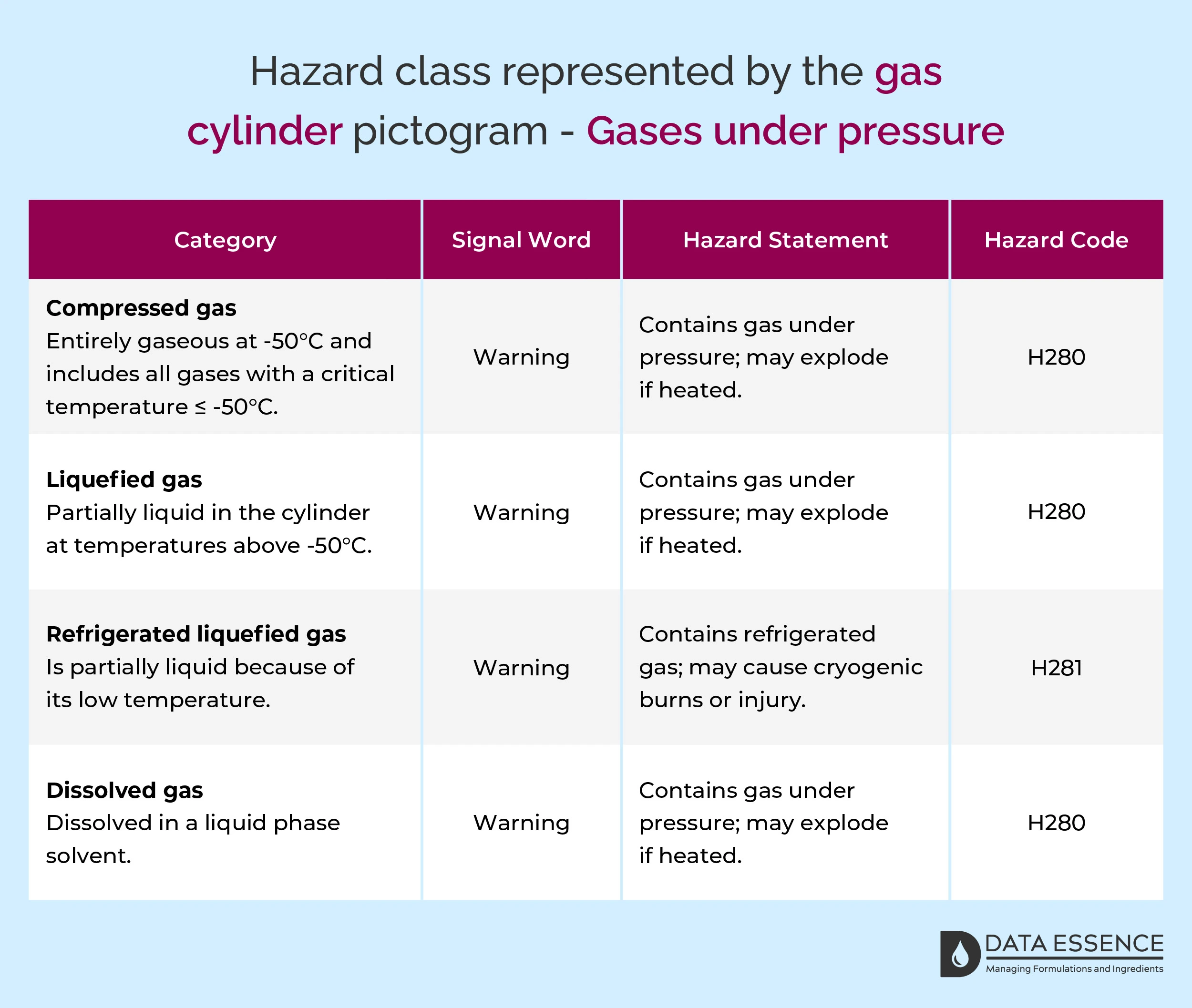
- Compressed gases: Notable examples include oxygen and helium. These gases remain in a gaseous state within their containers due to high pressure.
- Liquefied gases: Think of butane and carbon dioxide. They transition into a liquid state under pressure, allowing for storage at room temperature.
- Refrigerated liquefied gases (Cryogenic gases): Liquid nitrogen belongs here. These demand extreme cold to stay in a liquid form and require specialised handling.
- Dissolved gases: Acetylene is a prime example, existing in a liquid solvent. Handling differs from traditional gases.
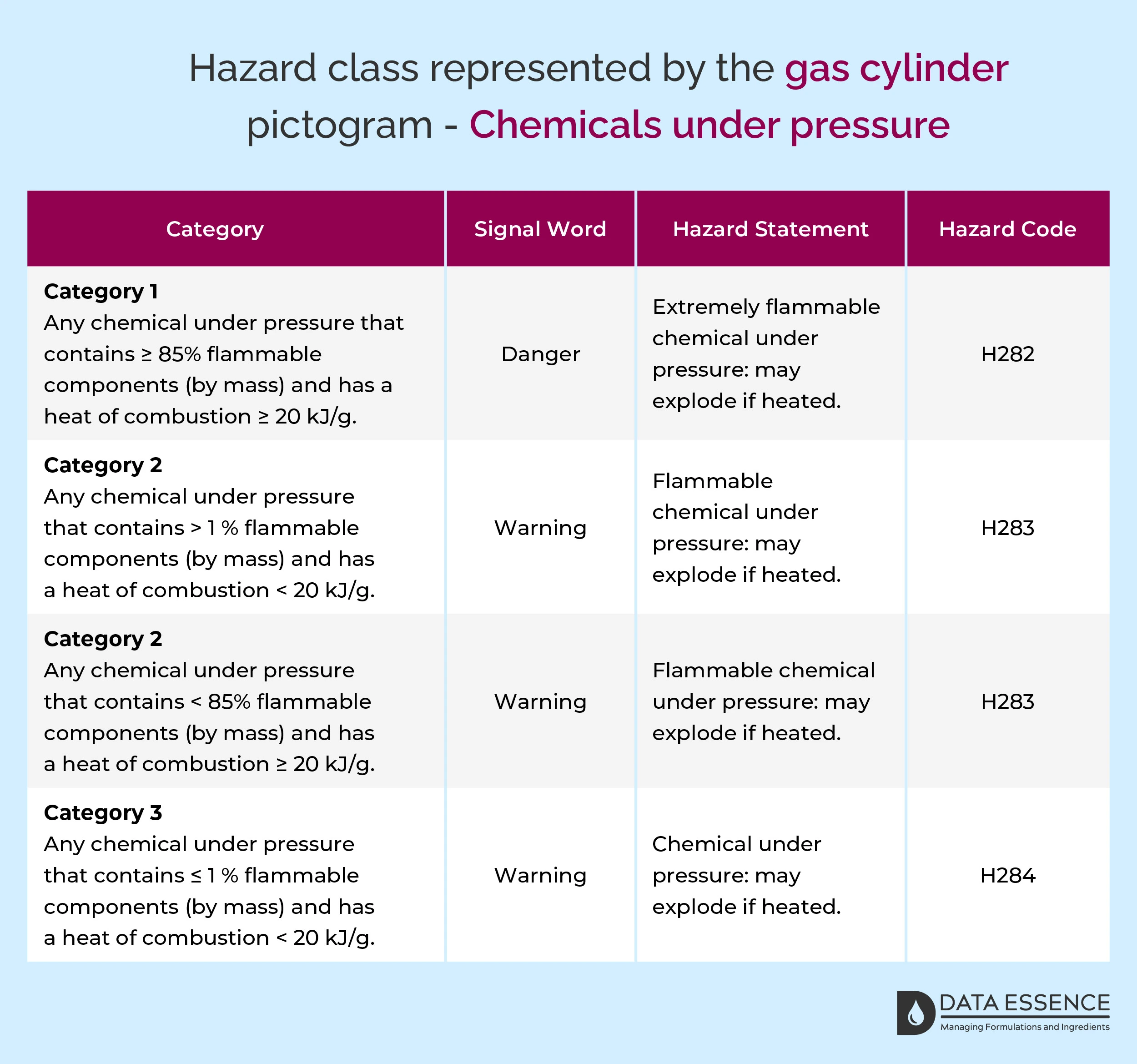
Moreover, chemicals under pressure constitute another category, comprising liquid or solid substances (like pastes or powders) with a gas pressurized at 200 kPa (kilopascal) or more at 20°C. These chemicals are further categorised based on flammable compound content and heat of combustion.
Understanding these classifications is fundamental for safe storage and handling in various industries, ensuring compliance with stringent safety protocols.
Hazard classes represented by the gas cylinder pictogram
The two Hazard Classes represented are ‘Gases under pressure’ and ‘Chemicals under pressure’. Take a look at each of these hazard classes in relation to signal words, hazard statements and hazard codes below.
Gases under pressure
Chemicals under pressure
The implications of gases under pressure
In a workplace setting, gases under pressure wield the potential for swift and substantial gas discharge, carrying the inherent risk of health and fire-related dangers, contingent upon the gas’s properties. Such discharge may occur either by a deliberate act of opening the cylinder valve or, more critically, through an inadvertent release stemming from a damaged or leaking valve.
Of concern is the prospect of damaged gas cylinders, capable of exhibiting forceful and uncontrolled movements like rockets or spinning projectiles. This unsafe scenario holds the potential to cause severe injuries and extensive damage, often manifesting when an uncapped or inadequately secured cylinder is knocked over, leading to the breakage of the cylinder valve.
The handling of refrigerated liquefied gases, commonly known as cryogenic gases, necessitates particular attention due to their exceptionally low temperatures. Exposure to these frigid substances can result in cryogenic burns or frostbite injuries, underscoring the importance of adhering to stringent safety protocols when dealing with such materials in the workplace.
Always consult the Safety Data Sheet (SDS) and product CLP label to thoroughly understand the risks associated with the specific product you are working with. When in doubt, seek clarification and ask questions to ensure safety.
Protective measures for gases under pressure
To safely handle products marked with the gas cylinder pictogram, follow these guidelines:
- Review safety information: Always consult the Safety Data Sheet (SDS) and product label to understand hazards and precautions. If uncertain, seek clarification.
- Consider substitutes: If feasible, replace hazardous products with less risky alternatives.
- Prevent gas release: Use products in well-ventilated areas and minimise quantities for tasks.
- Protect your eyes: Wear chemical safety goggles or face shields when working with pressurised gases.
- Proper PPE training: Employers should train workers on selecting, wearing, and maintaining personal protective equipment (PPE) as indicated in the SDS.
- Gas cylinder handling: Inspect cylinders and valves for damage. Use suitable regulators and secure cylinders upright. Keep valves closed when not in use. Avoid adding lubricants or tape to valves. Prevent contamination.
- Safe transportation: Use proper equipment to move cylinders and avoid dropping or banging them.
- Refrigerated liquefied gases: Wear cold insulating gloves, a face shield, or eye protection. Refrain from wearing accessories that can freeze to skin if exposed to cold gas. Ensure equipment can withstand low temperatures and cool receiving containers beforehand.
- Awareness: Maintenance personnel should be informed about potential hazards and required precautions before commencing work.
Safe storage for gases under pressure
- Sunlight protection: Shield from direct sunlight and ensure well-ventilated storage.
- Incompatible materials: Keep away from incompatible substances and potential ignition sources.
- SDS guidance: Adhere to SDS instructions, including storage quantities, temperature requirements, and separation distances.
- Leak detection: Consider using leak detection and alarm systems for added safety.
- Warning signs: Post warning signs and keep cylinders clear of exits.
- Secure upright position: Store cylinders upright, securely fastened with valve protection caps intact.
- Limit quantity: If possible, avoid storing excessive quantities.
- Follow supplier recommendations: Respect supplier-recommended storage durations.
- Label and inventory: Label containers with received, opened, and disposal dates, and use a first-in, first-out inventory system.
- Dispose promptly: Properly dispose of “empty” or unlabelled cylinders in a timely manner.
- Regulatory compliance: Comply with relevant by-laws, Fire Codes, and workplace safety regulations in your jurisdiction.
Conclusion
By acknowledging the potential risks associated with gas cylinders, such as leakages and fire hazards, and implementing appropriate safety measures, we create a safer working environment for employees and minimise the possibility of accidents. Storing, transporting, and handling these products in accordance with the gas cylinder pictogram guidelines is essential to protect not only our employees but also our customers and the environment.