Whether you already handle products that are acutely toxic or are simply interested in learning more about the necessary safety precautions, this blog post will provide you with valuable insights to protect yourself and others from potential hazards.
What does the skull and crossbones pictogram mean?

What are acutely toxic substances?
Acute toxicity relates to effects that may occur under the following conditions:
- Following skin contact or ingestion of a single dose of a substance.
- Multiple doses administered within a 24-hour timeframe.
- Inhalation exposure lasting 4 hours.
Acute toxicity can arise from direct exposure to the product or contact with a product that, upon contact with water, releases a gaseous substance capable of causing acute toxicity.
Hazard class represented by the skull and crossbones pictogram
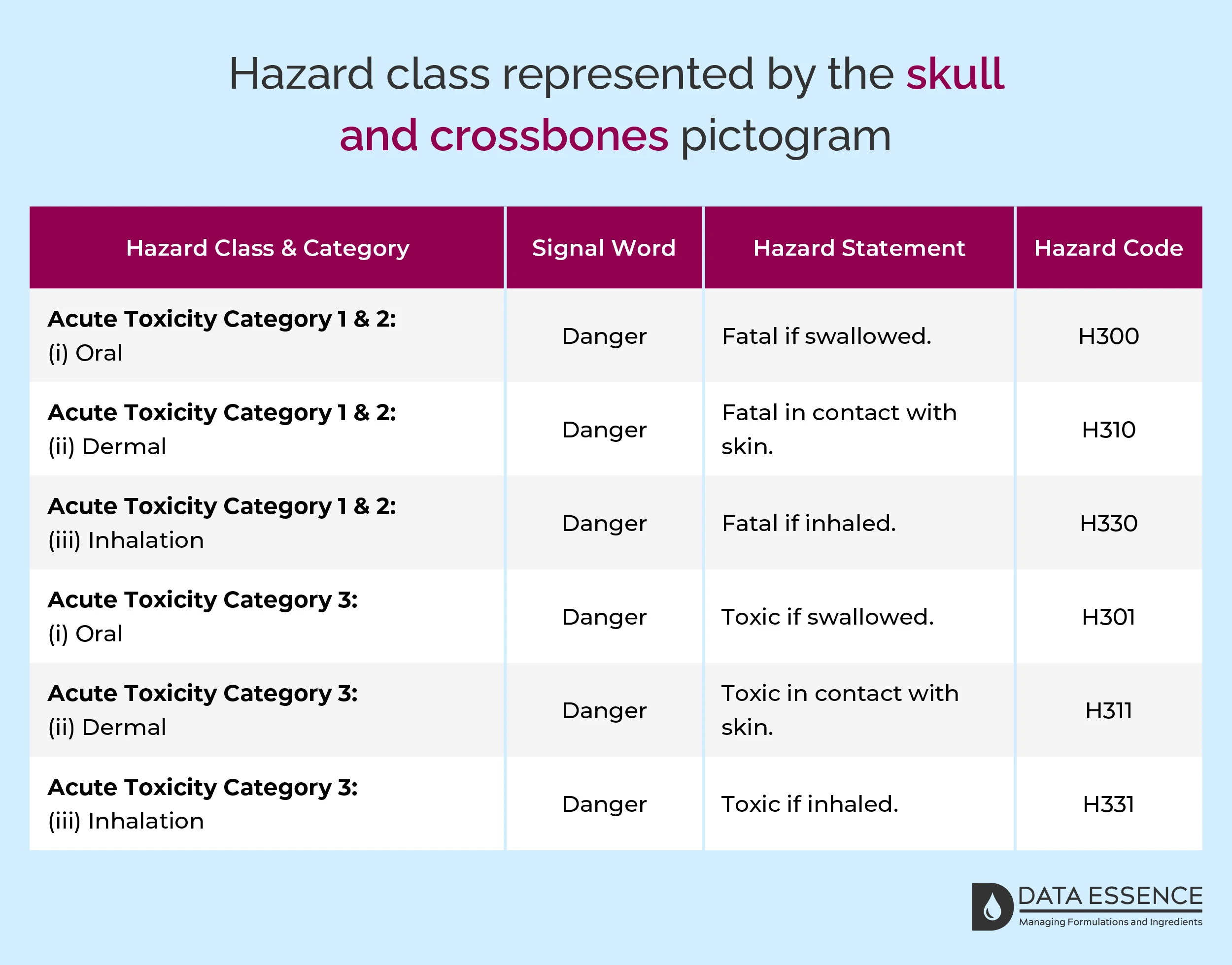
The implications of acutely toxic substances
Apart from the hazards indicated by the skull and crossbones pictogram, it is crucial to consider that a product might pose additional risks. These could include:
- Other health hazards, like skin corrosion or irritation, carcinogenicity, or specific target organ toxicity (single or repeated exposures).
- Physical hazards, such as being corrosive to metals, flammable, or reactive.
Always consult the Safety Data Sheet (SDS) and product CLP label to thoroughly understand the risks associated with the specific product you are working with. When in doubt, seek clarification and ask questions to ensure safety.
Protective measures for acutely toxic substances
- Personal hygiene: After handling these substances, practice thorough handwashing as a basic safety measure. Ensure that no residue remains on your skin.
- Eating, drinking, and smoking: Under no circumstances should you eat, drink, or smoke while working with these products. Maintaining strict separation between these substances and consumables is non-negotiable.
- Swallowing: In the unfortunate event of swallowing any of these toxic substances, immediate action is crucial. Contact a poison centre or a qualified doctor/physician for advice. Rinse the mouth thoroughly and remove any contaminated clothing promptly.
- Clothing handling: Any clothing that comes into contact with these substances should be handled with caution. Wash contaminated clothing thoroughly before reuse to prevent any potential risks.
- Eye and skin contact: Avoid getting these substances in your eyes, on your skin, or on your clothing. The use of personal protective equipment is imperative.
- Personal protective equipment: When handling toxic substances marked with the skull and crossbones symbol, wear protective gloves, suitable clothing, and eye and face protection to minimise direct contact.
- Inhalation risk: Avoid inhaling any dust, fumes, gas, mists, vapours, or sprays generated by these substances. Usage should ideally be restricted to outdoor environments or well-ventilated areas.
- Respiratory protection: As an additional precaution, consider wearing respiratory protection to safeguard against any inadvertent inhalation of toxic fumes.
- Inhalation incident: If someone accidentally inhales these substances, swiftly move them to an area with fresh, uncontaminated air. Ensure they remain at rest in a position conducive to normal breathing.
- Secure storage: To prevent unauthorised access and to maintain a heightened level of safety, store these substances securely in a locked area designated for hazardous materials.
Safe storage for acutely toxic substances
- SDS guidance: Be attentive to any specific storage requirements; refer to the SDS for guidance.
- Storage: For substances posing inhalation hazards, store them in well-ventilated areas with tightly closed containers.
- Storage conditions: Maintain a cool, dry storage location, away from direct sunlight and exit paths, and display warning signs.
- Secure storage: Store the product securely in a locked area.
- Limit quantity: Whenever possible, avoid stockpiling and limit the quantity stored.
- Maintain safe storage: Regularly inspect containers and storage areas for signs of leaks or damage. Use trays made of compatible materials to contain spills or leaks.
- Empty containers: Keep empty containers separate and securely closed, as they may still contain hazardous residue.
- Storage height: Place containers at a convenient height for handling, preferably below eye level to reduce the risk of accidents.
- Safety: Ensure ready access to appropriate firefighting and spill cleanup equipment.
- Regulatory compliance: Comply with all relevant health and safety regulations, as well as fire and building codes.
Conclusion
By acknowledging the potential risks associated with acutely toxic substances, such as causing fatality or toxicity after being swallowed, absorbed through the skin, or being inhaled, and implementing appropriate safety measures, we create a safer working environment for employees and minimise the possibility of accidents. Storing, transporting, and handling these products in accordance with the skull and crossbones pictogram guidelines is essential to protect not only employees but also customers and the environment.

